Seeds of confusion: Why is my pomegranate’s fruit so pale?
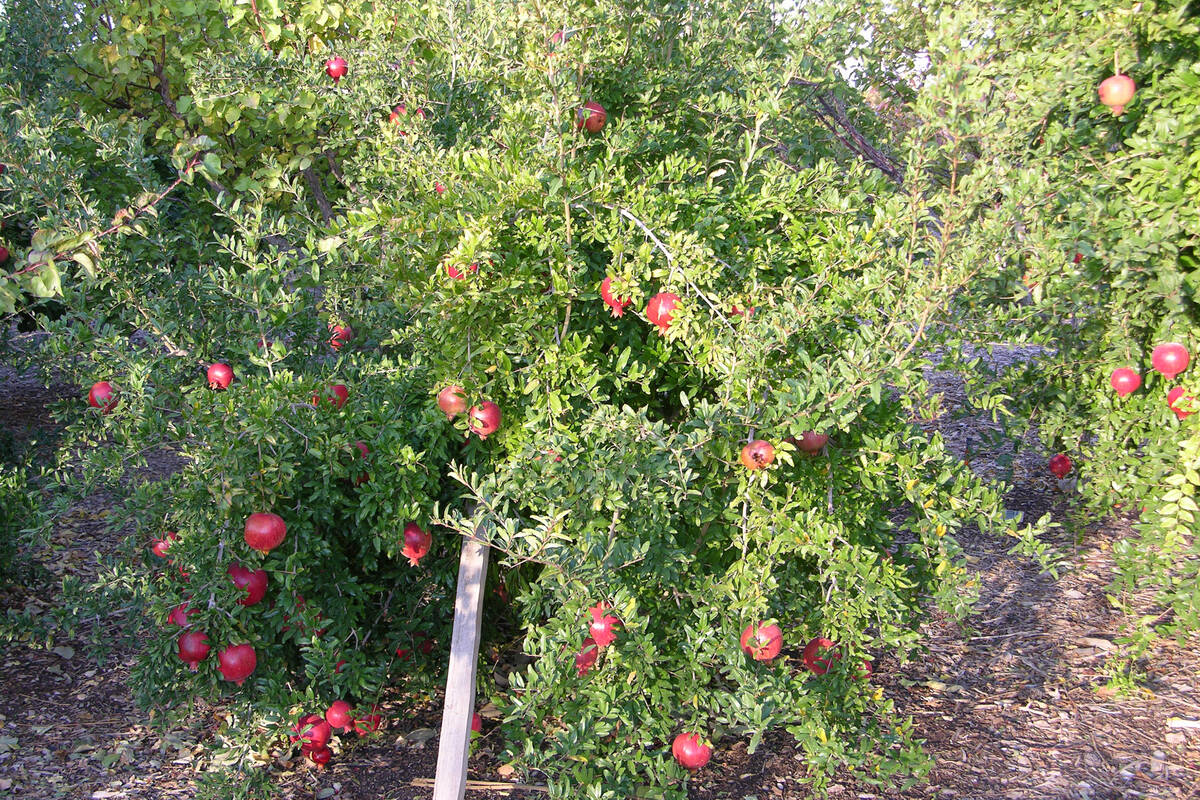



Q: I have a Wonderful pomegranate that is 3 years old. All this time I have been waiting for bright red arils. The fruit from this tree is almost yellow to a light pink and does not smell or look moldy. The fruit tastes fine, but I was worried about eating them. If I understand correctly this might be the way the fruit will look all the time and it is OK to eat. I also have a younger Utah Sweet pomegranate but have yet to get any fruit that lasted after heavy winds.
A: I am familiar with Wonderful and Utah Sweet pomegranates. Wonderful produces fruit around Halloween, and Utah Sweet produces around late September. The inside of Wonderful should be dark red, a very pretty fruit and very puckery. The inside of Utah Sweet should be pinkish or white with red streaks, not as pretty and not as puckery. I would not be afraid to eat off-color fruit unless the inside was moldy.
All of your pomegranates should be producing fruit in three to five years. With careful pruning, the fruit should get larger as it gets older and as the remaining stems grow bigger.
Are you sure these trees were not mixed up? The fruit sounds backward to me. Utah Sweet is a soft-seeded variety and can vary in color from white to pink. The Wonderful variety should have hard seeds, and the pulp should be dark red throughout.
As a side note, make sure that you remove any suckers from the base. It won’t affect the quality of the fruit, but it will affect its eventual size. All pruning should begin at the bottom, first by removing the suckers.
The biggest problem facing pomegranates is leaf-footed plant bugs and the fungal disease they carry from fruit to fruit. Hopefully your pomegranates were surrounded by 2 to 3 inches of wood chips. These wood chips add an extra day to the irrigation it needs during summer months and improve the soil. In normal years, deep irrigation occurs once a week or less often during the winter and climbs to three or four times per week by midsummer. The water applied around the trees should penetrate to a depth of 18 inches. Usually, four or five drip emitters 12 inches from the base are enough to spread the water out.
This was not a normal year. Try withholding fertilizer applications next year to see if that helps kick-start production.
Q: Is it too late to start a cutting from a geranium and put it outside to root?
A: November is a bit too late. Geraniums prefer cooler weather (not cold). I would expect to start cuttings from a mother plant in late September or early October in most years. Timing is important. The other time to start them is late January or early February as it is still cooler but the soil is starting to warm up.
To take cuttings, cut off the last 6 inches of new growth and remove all but the newest leaves from the top or side branches. When you look at it, there should be a tuft of green at the top of the cutting. Rolling the stems into a powdered rooting hormone is a good idea but not necessary. Cuttings from this plant will root easily.
Nighttime soil temperatures of 55 to 60 degrees or warmer will get these cuttings to root. Until you get the hang of it, use a soil thermometer.
Stick these cuttings into clean potting soil. A good quality bagged potting soil works the best. Make sure this soil is clean of weed seeds and plant diseases. Using a pencil to open the soil, carefully stick these cuttings about one-third of the way (2 to 3 inches) into this soil. Close the soil back up by pressing it together. Make sure the soil drains easily and stays free of plant disease.
Q: What vegetables can be planted in raised beds now?
A: The cool-season vegetables (beans, beets, lettuce, radishes, etc.) start producing around October. Start with the harvest date. The longer it takes to harvest what you want, the earlier you should start planting. For instance, radishes are a cool-season crop. Radishes take about 30 days before harvesting. You should start planting radishes sometime in September (watch the weather). If you’re planting beets (also a cool-season crop), it takes around 45 to 50 days until harvest. For an October or early November harvest, plant them around the middle of September, weather permitting.
The warm-season vegetables (tomatoes, eggplant, peppers, cucumbers, melons, etc.) are either planted in the spring or early fall in our climate. When planting in the spring, soil temperature is the limiting factor. “Fluff up” the soil and get it ready for planting. Fluffy soil warms up faster than unfluffed soil. If planting from seed, remember that seeds like a firm seedbed. After you’re finished, firm the soil. This can be done with an irrigation or two so water the soil before planting.
Bob Morris is a horticulture expert and professor emeritus of UNLV. Visit his blog at xtremehorticulture.blogspot.com. Send questions to Extremehort@aol.com.